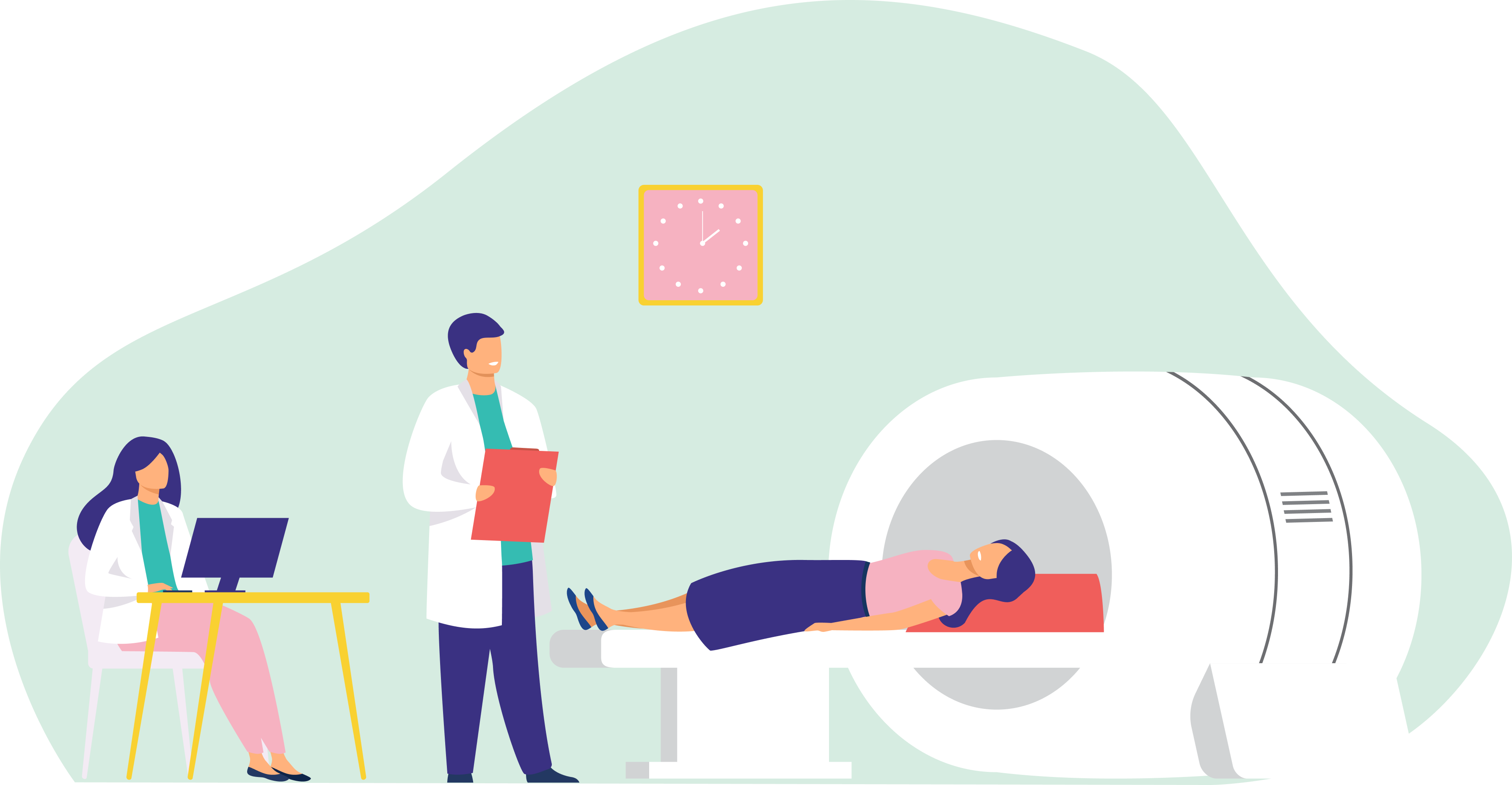
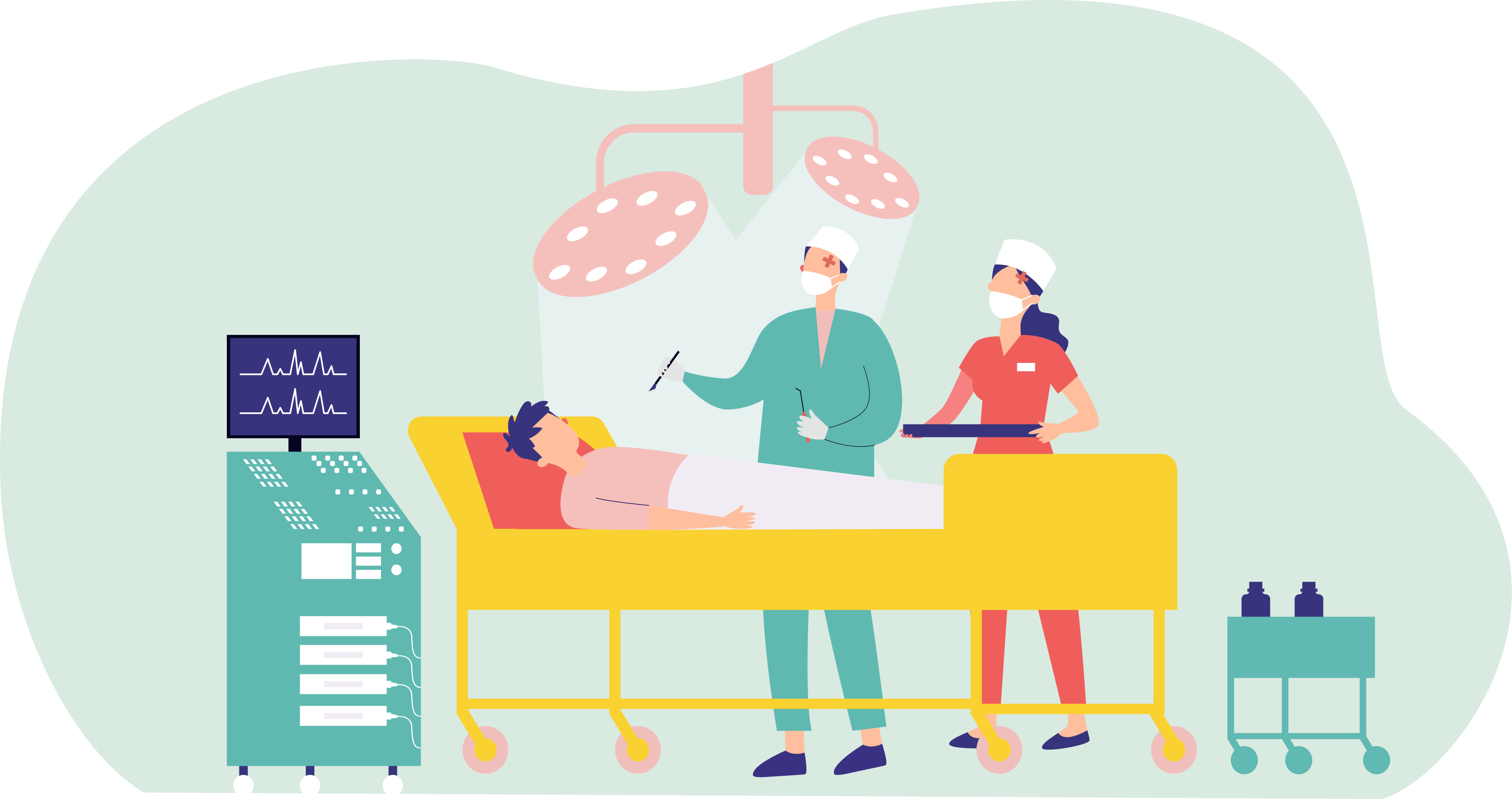
Diagnostic Radiographers use medical radiation equipment to produce images of the human body.
Diagnostic Radiographer Job Description
- Assist in treatment procedures.
- Produce clear radiographic images using X-ray equipment, Computerised Tomography (CT), and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machines.
- Prescribe the right dosage of radiation to a patient under radiation safety regulations.
- Organise the storage of radiographic images so that medical professionals can easily access them.
- Manage Teleradiology (when radiographic images are transferred from one location to another).
Note
Machines that produce radiation are lined with lead, which protects radiographers and patients. So don't worry, you're safe!
What you should know about Diagnostic Radiographer jobs in Singapore
Nature of Work
The ability to speak other languages and local dialects will also be helpful when you need to talk to elderly patients.Key advice
Always approach your patients with empathy and understanding as your demeanour significantly impacts their experience.-
Entry RequirementsEntry Requirements
- Take up attachments or shadow a senior Diagnostic Radiographer.
- In Singapore, only the Singapore Institute of Technology (SIT) and Parkway College offer a Bachelor of Science in Diagnostic Radiography.
-
Possible PathwayPossible Pathway
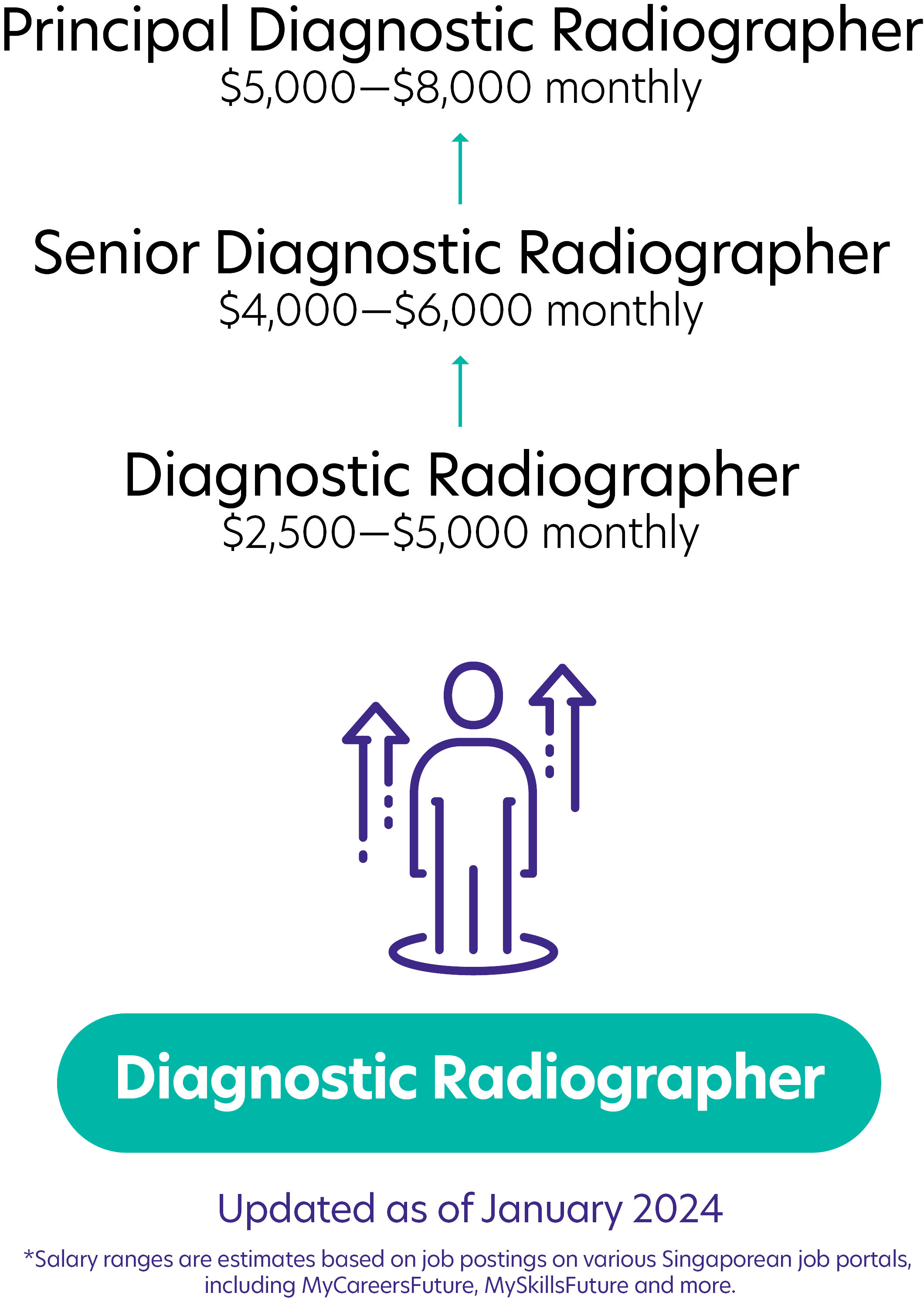
Skills you need to pursue a Diagnostic Radiographer career in Singapore
Operate Medical Machinery
Proficiency in operating medical imaging equipment, including MRI machines, X-rays and CT scanners.Image Analysis
Develop the ability to analyse and interpret radiographic images to provide reliable data for diagnoses.Radiation Safety
Gain expertise in radiation physics and safety practices to measure and control radiation doses for safety.Communication
Excellent communication skills for effectively explaining procedures to patients, understanding their concerns.Attention to Detail
Meticulous attention to detail in capturing, evaluating and recording imaging results for accurate diagnoses.Empathy
A strong sense of empathy to provide compassionate care for patients who may be anxious or uncomfortable.
“Though the time that I spend with my patients is brief, my job is extremely satisfying.”
G Vicneswari, Diagnostic Radiographer
Related Job Roles
Explore Other Programmes
Browse AllYou have bookmarked your first item!
Find it in My Discoveries with insights on your interests!