Microbiologists oversee Microbiology laboratory activities. It involves sampling, testing, and monitoring for environmental cleanliness and product quality.
Microbiologist (Quality Control Analyst) Job Description
- Manage laboratory supplies, samples, and testing.
- Conduct Microbiological testing to review results and receive approval.
- Carry out systematic documentation according to Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) and the Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP).
- Maintain the accuracy of laboratory instruments.
- Prepare and revise procedures to maintain validation.
Note
Microbiologists will work with a team to ensure that every batch of food/drugs/Medical devices that are released will benefit the consumers/patients. It’s a long and complex process for food/drug/Medical devices to be approved for manufacturing.
What you should know about Microbiologist (Quality Control Analyst) jobs in Singapore
Nature of Work
As Microbiologists, you will engage in the research and study of microorganisms to understand their effect on humans, animals and the environment.Key Advice
Stay up to date with the latest advancements in the field and maintain meticulous attention to detail in laboratory practices.-
Entry RequirementsEntry Requirements
- Minimally a diploma in a Microbiology-related field is required.
- For the manager-level role, you may require a degree in a Microbiology-related field or at least three to five years of work experience.
- For lab or practical experience, engage in internships or joint research.
-
Possible PathwayPossible Pathway
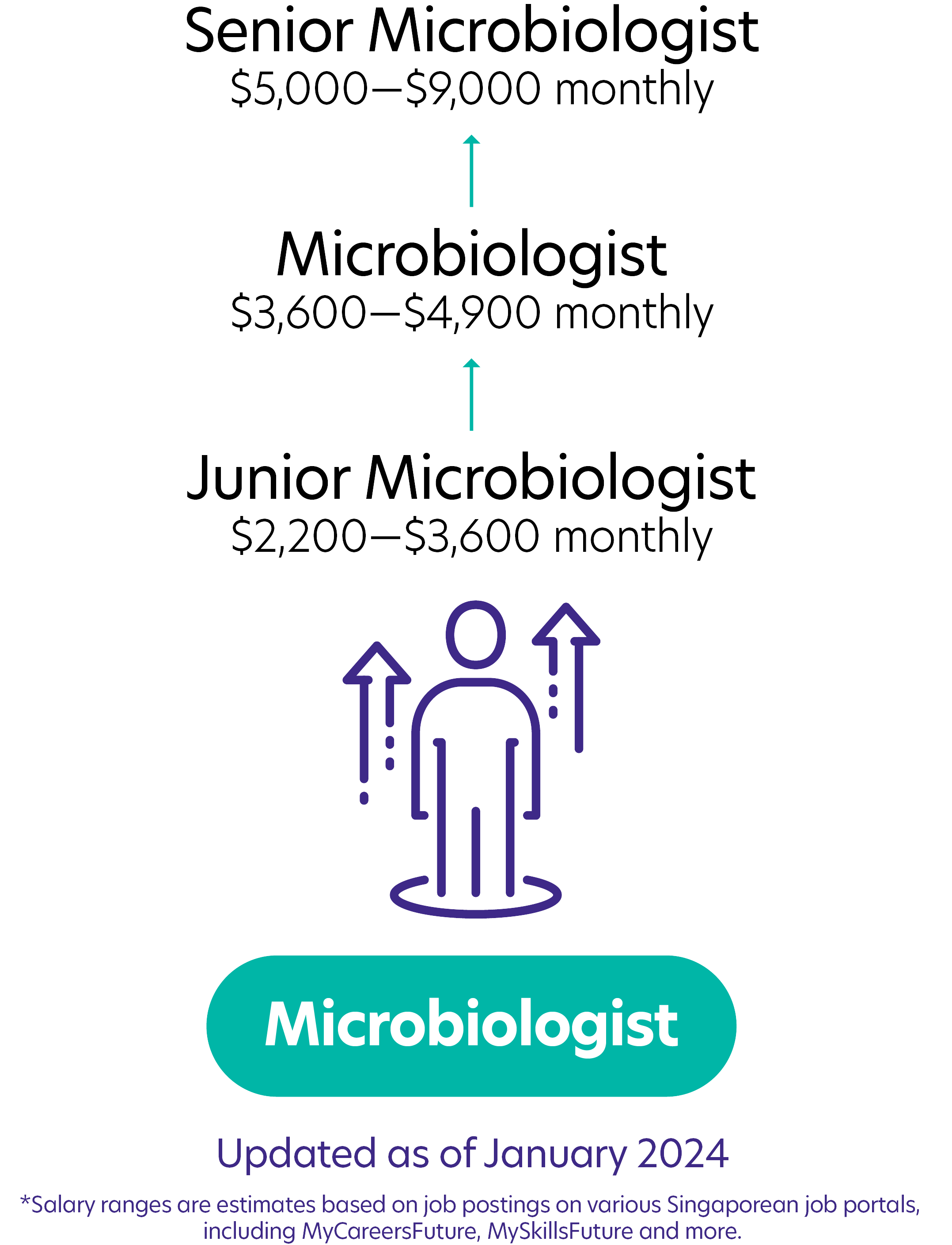
Skills you need to pursue a Microbiologist (Quality Control Analyst) career in Singapore
 Hard Skills
Hard Skills
Microbiology Techniques
Proficiency in Microbiological methods, including culturing, isolation, and identification.Aseptic Technique
Expertise in maintaining a sterile environment to prevent contamination during Microbiological procedures.Analytical Technique
Skilled in the precise analysis of samples using various Microbiological and Biochemical testing methods.Communication
Effective in conveying complex Microbiological concepts and findings to different types of audiences.Problem-Solving
Strong ability to identify and find solutions for challenges in Microbiological research and analysis.Decision Making
Competent in making informed decisions based on scientific data, often under time-sensitive conditions.Related Job Roles
Explore Other Programmes
Browse AllYou have bookmarked your first item!
Find it in My Discoveries with insights on your interests!



