Geospatial Analysts study and analyse Geographic data. They present their findings to key stakeholders and collaborate to generate solutions.
Geospatial Analyst Job Description
- Extract, compile and analyse Geospatial data.
- Generate actionable insights that enable data-informed urban planning for Singapore.
- Collaborate with a variety of industry professionals to understand planning problems.
- Conduct analytic studies and develop relevant digital tools to form insights and discover new solutions.
- Organise workshops and conduct training to equip others with spatial planning analytics.
Note
Geospatial Analysts play a crucial role in identifying current and potential threats of climate change to Earth.
What you should know about Geospatial Analyst jobs in Singapore
Nature of Work
As Geospatial Analysts, you will use data for tasks varying by sector, with urban planning focusing on understanding and predicting urban growth.Key Advice
As Geospatial Analysts in Climate Science, you will compile Geographical data to identify and monitor climate change threats.-
Entry RequirementsEntry Requirements
- A degree in Geology, Environmental Studies or related fields is preferred.
- Proficiency in mapping tools like ArcGIS, QGIS and Pix4D.
- Adept in GIS is the most common requirement, but companies might require proficiency in other Geospatial technologies, such as Geofencing and Remote Sensing.
-
Possible PathwayPossible Pathway
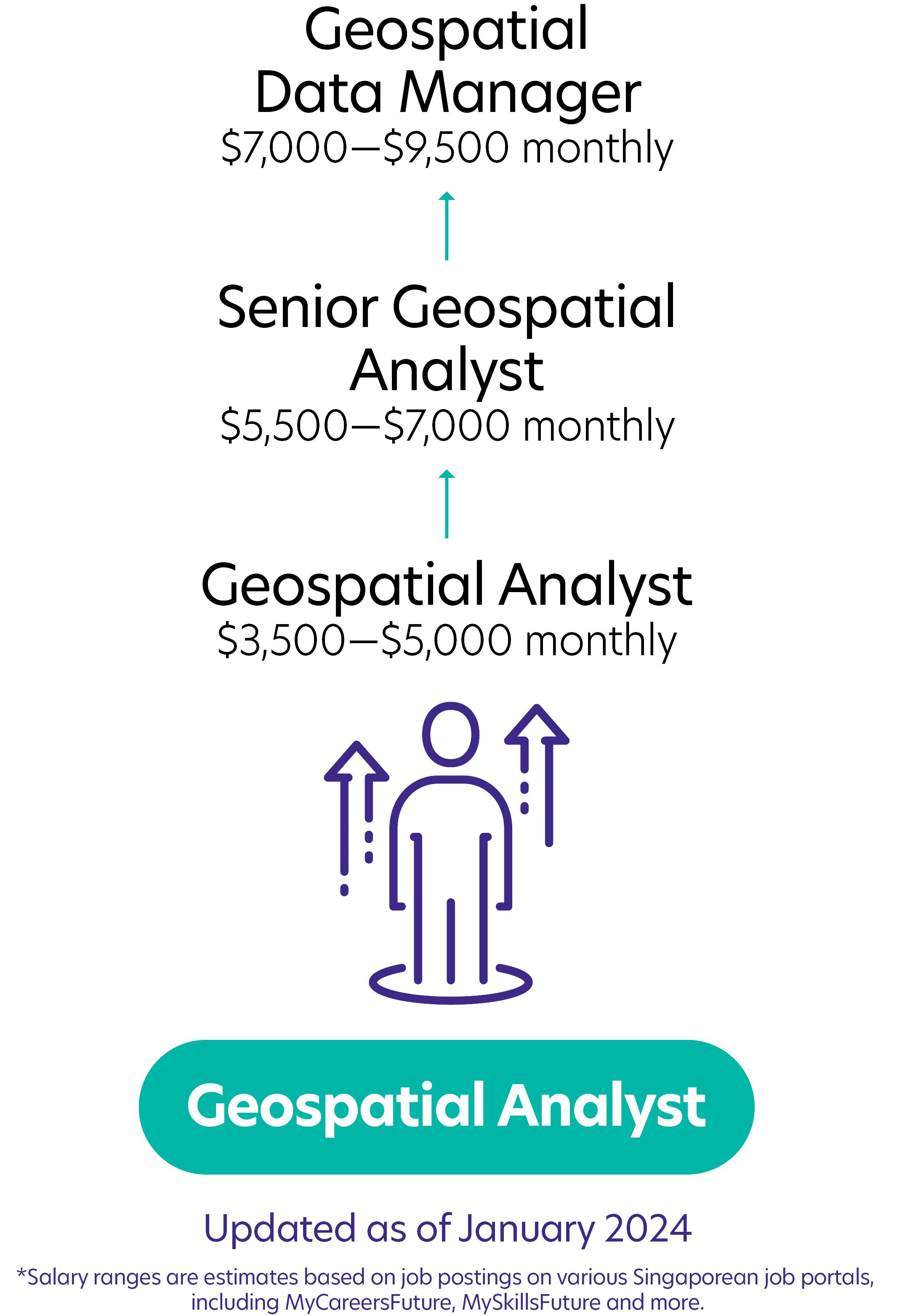
Skills you need to pursue a Geospatial Analyst career in Singapore
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Use Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for accurate mapping in Geospatial projects.Model and Map Construction
Construct intricate Geospatial models and maps to facilitate comprehensive spatial analysis.Database Management
Manages Geospatial databases to ensure seamless Geospatial operations and reporting.Communication Skills
Exhibits strong communication skills to inform team members and stakeholders.Teamwork
Collaborates seamlessly within teams, fostering a cooperative and synergistic environment to achieve common goals.Problem-Solving
Identifies and resolves complex issues to overcome challenges and obstacles.Related Job Roles
Explore Other Programmes
Browse AllYou have bookmarked your first item!
Find it in My Discoveries with insights on your interests!