Pharmacists use their expert knowledge of drugs to market, develop, research, and supply medicine to patients.
Pharmacist Job Description
- Conduct clinical trials and tests to appraise and examine the characteristics and purity of drugs.
- Provide drugs based on a doctor's prescription and ensure that those drugs are safe to take.
- Inform patients on possible drug side effects and medicine a patient may use for self-medication.
- Maintain the pharmacy's supply of drugs and ensure that every drug (from the smallest pills to the bottles) is accounted for.
- Oversee and synchronise the work of pharmacy technicians, pharmacy assistants, and pharmacists in training.
Note
Pharmacists can take up specialisations in certain areas (e.g. medicine for cancer treatment) during their postgraduate studies, after they have obtained their bachelor's degree.
What you should know about Pharmacist jobs in Singapore
Nature of Work
Pharmaceutical Sciences focus on the research and development side while as Pharmacists, you will compound and dispense medicine.Key Advice
Always prioritise patient safety by double-checking prescriptions and being vigilant about potential drug interactions.-
Entry RequirementsEntry Requirements
- You will need a Singapore degree in Pharmacy with minimally 12 months of experience in a practical Pharmacy. Or a Pharmacy qualification from overseas institutions recognised by the Singapore Pharmacy Council (SPC).
- You may also take up the National University Healthcare System (NUHS) Allied Health job shadowing programme.
-
Possible PathwayPossible Pathway

Skills you need to pursue a Pharmacist career in Singapore
Medical Dispensing
Expertise in accurately dispensing prescription medications, ensuring correct dosage and adherence to safety.Practical Mathematics Skills
Proficiency in Mathematics is essential for calculating precise drug quantities and dosages.Proficiency in Handling Fine Equipment
Skilled in using measuring devices to accurately prepare and dispense medications.Attention to Detail
Meticulous attention to detail, vital for ensuring accuracy in medication dispensing and avoiding errors.Communication
Strong communication skills to effectively counsel patients about medication usage.Problem-Solving
Ability to solve problems, such as addressing prescription discrepancies and providing solutions.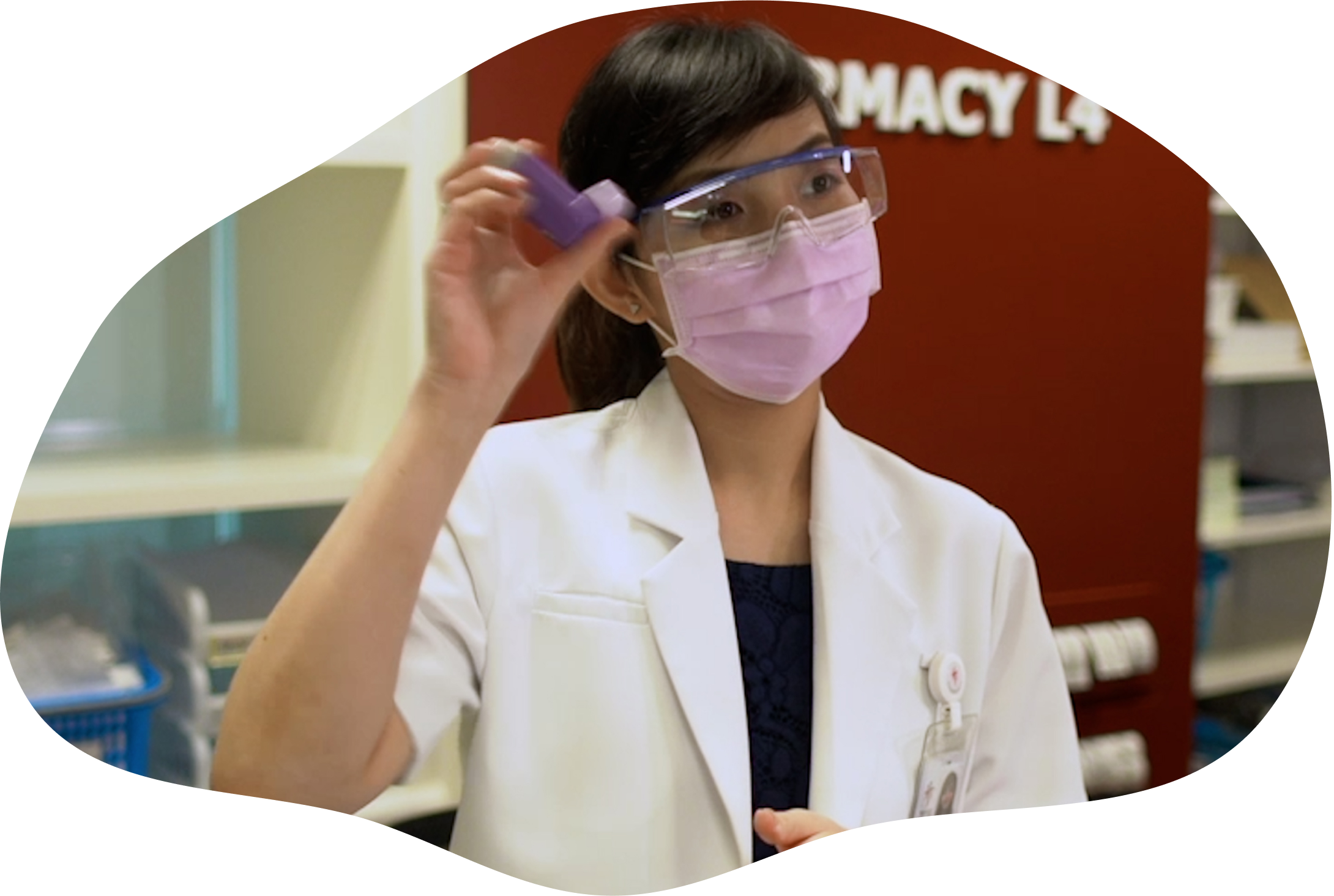
“It takes time and effort to be a Pharmacist but it's a job that makes a difference to others' lives. ”
Yi San, Pharmacist
Related Job Roles
Explore Other Programmes
Browse AllYou have bookmarked your first item!
Find it in My Discoveries with insights on your interests!