Biologists cover a broad area within Life Sciences. Biologists study the origin, development, structure, and function of a plant or animal life.
Biologist Job Description
- Collect organism samples (e.g. tissue cells), measurements, photographs, or sketches.
- Perform experiments on specific plants, animals, or ecosystems.
- Record and maintain experiment results.
- Analyse experimental results on the organism to learn its behaviour and impact on its surroundings.
- Develop experimental protocols for conducting the project.
Note
Government support for Biologists is available under the SGUnited Traineeships Programme for new and recent graduates where they can develop skills and receive a training allowance.
What you should know about Biologist jobs in Singapore
Nature of Work
Many types of Biologists cover different aspects of life. As Biologists specialising in a specific area or feature, you will be named according to your speciality!Key Advice
Stay curious and open-minded; the field of Biology is vast and constantly evolving, so continuous learning is key to success.-
Entry RequirementsEntry Requirements
- Minimally a bachelor’s degree or equivalent in the Biology field.
- Pursue your education based on the broad area of specialisation that you are interested in, such as Zoology (the study of animals) or botany (the study of plants).
- Having a strong understanding of scientific concepts, including Biology and Chemistry, laboratory equipment and laboratory procedures.
-
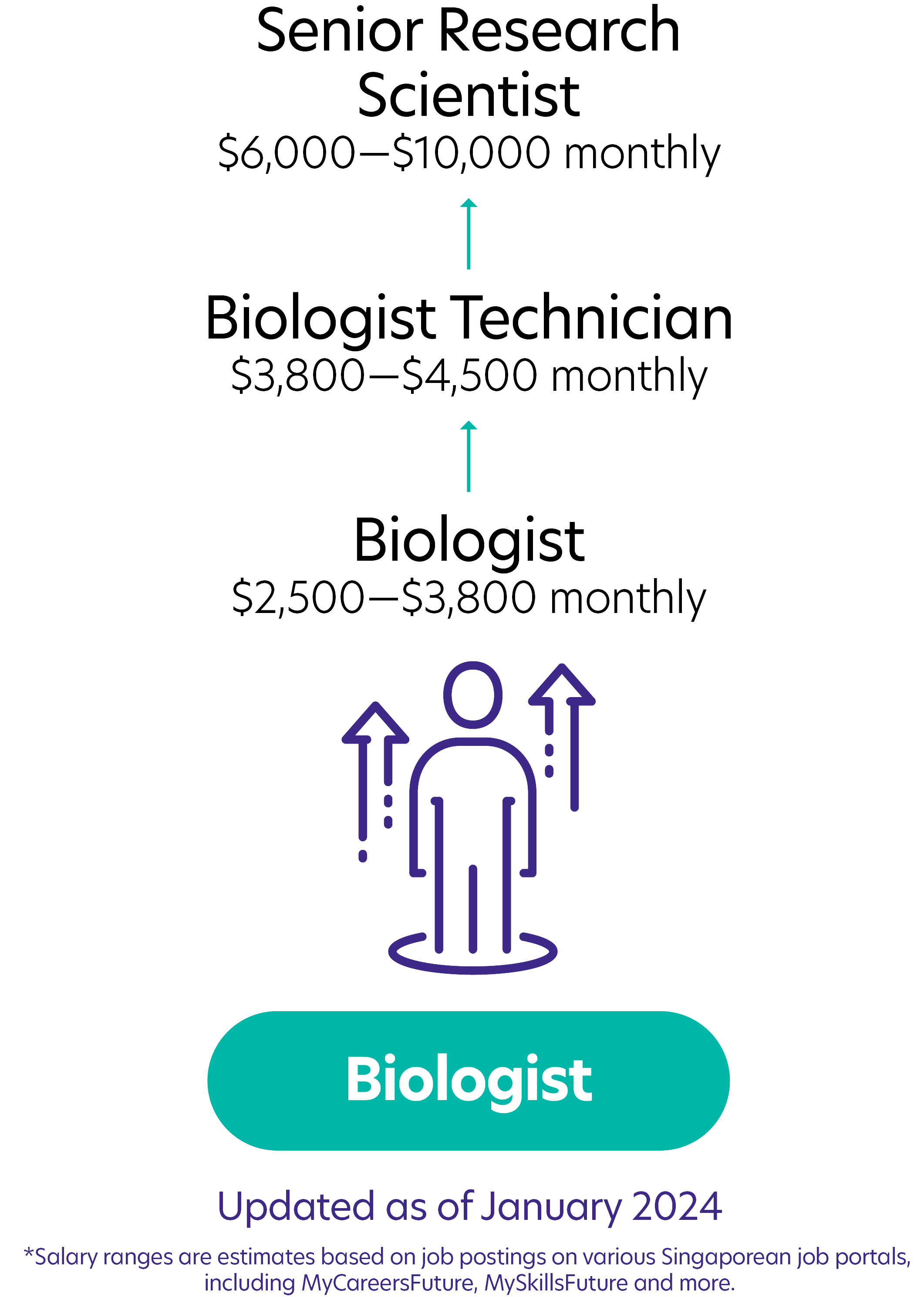
Possible PathwayPossible Pathway
Skills you need to pursue a Biologist career in Singapore
Biorisk Management
Understand risks associated with research, such as handling pathogens or genetically modified organisms.Laboratory Management
Organisational and operational aspects of running a lab and ensuring compliance with safety protocols.Chemical Risk Management
Safe handling and disposing of chemicals and complying with regulations regarding chemical use.Communication
Essential for presenting research, writing reports and papers, and collaborating with colleagues.Problem-Solving
Identify research questions, develop hypotheses, and design experiments to test their validity.Collaboration
Important for working effectively in teams, sharing knowledge, and combining expertise from different areas.Related Job Roles
Explore Other Programmes
Browse AllYou have bookmarked your first item!
Find it in My Discoveries with insights on your interests!










