Biomedical Engineers study and develop solutions to improve the quality of medical care products.
Job Responsibilities
- Design, install, and implement Biomedical equipment and systems.
- Train Clinicians and other staff on the proper use of Biomedical equipment, ensuring the safe and effective utilisation of the equipment to deliver optimal patient care.
- Maintain equipment and solve technical problems by performing preventive maintenance on equipment and conducting regular inspections.
- Conduct research and evaluate Engineering aspects of Biomedical treatment techniques.
Note
From creating revolutionary medical devices to advancing tissue Engineering, Biomedical Engineers are at the forefront of innovations that improve patient care and treatment outcomes.
What you should know about Biomedical Engineer jobs in Singapore
Nature of work
As Biomedical Engineers, your job involves working on a lot of cool things, from surgical robots to 3D printing of organs.Key advice
There is a lot to learn! You must read up on scientific concepts and processes related to solutions they are developing.-
Entry RequirementsEntry Requirements
- A bachelor's degree in Biomedical Engineering is preferred.
- Apply for internships to learn and gain hands-on experience in Biomedical Engineering operations.
-
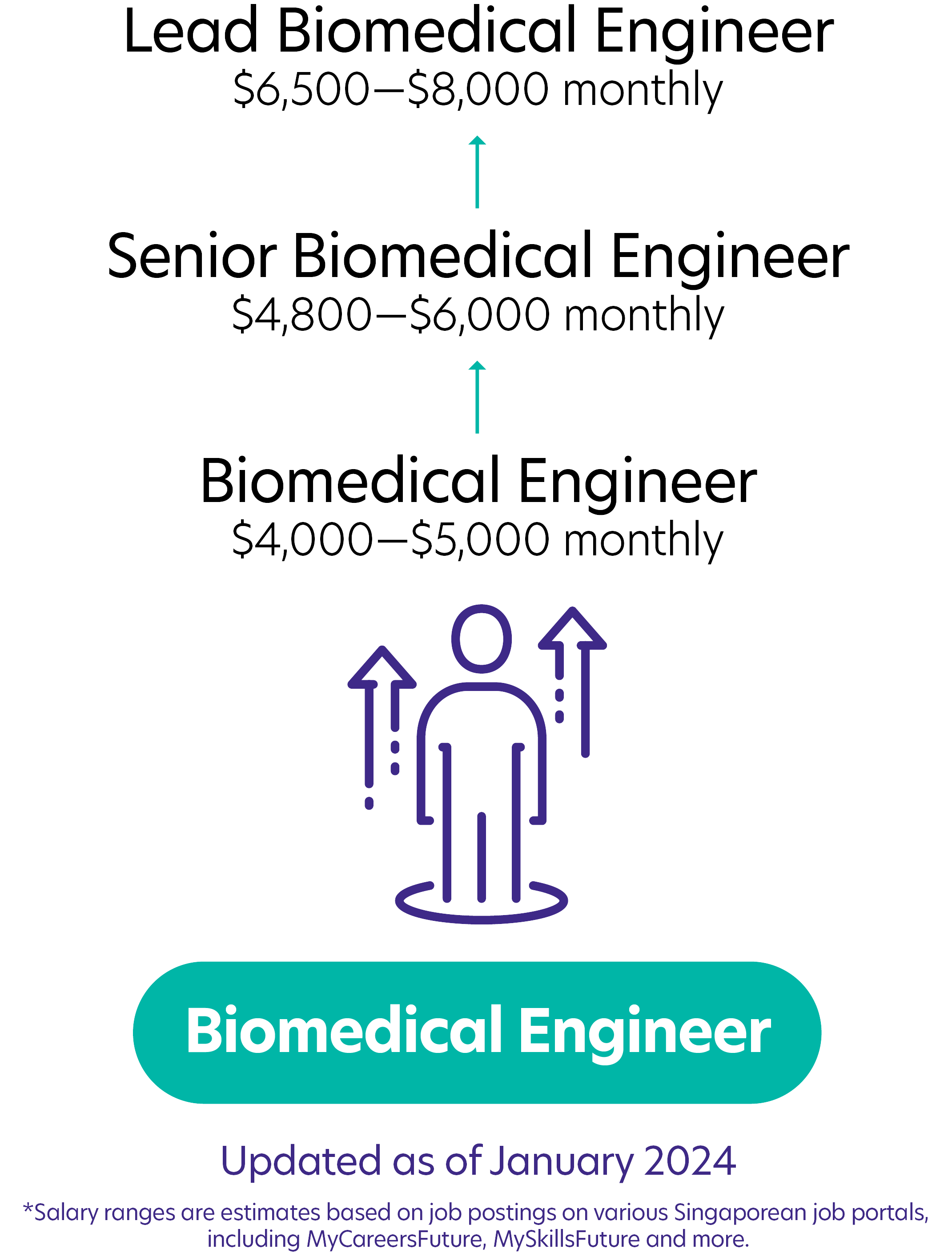
Possible PathwayPossible Pathway
Skills you may need
Medical Imaging
Proficient in technologies like MRI and X-rays, with skills in developing and improving these imaging tools.Engineering Principles
Strong foundation in Engineering principles, applying them to solve Healthcare problems.Product Development
Adept in the cycle of medical product development, from initial design, testing and final market release.Collaboration
Excellent teamwork skills are necessary to collaborate with Healthcare professionals and Engineers.Decision Making
Ability to make informed, ethical decisions in complex situations, balancing feasibility and patient safety.Problem-Solving
Creative and analytical problem-solving skills are crucial for tackling challenges in the Biomedical field.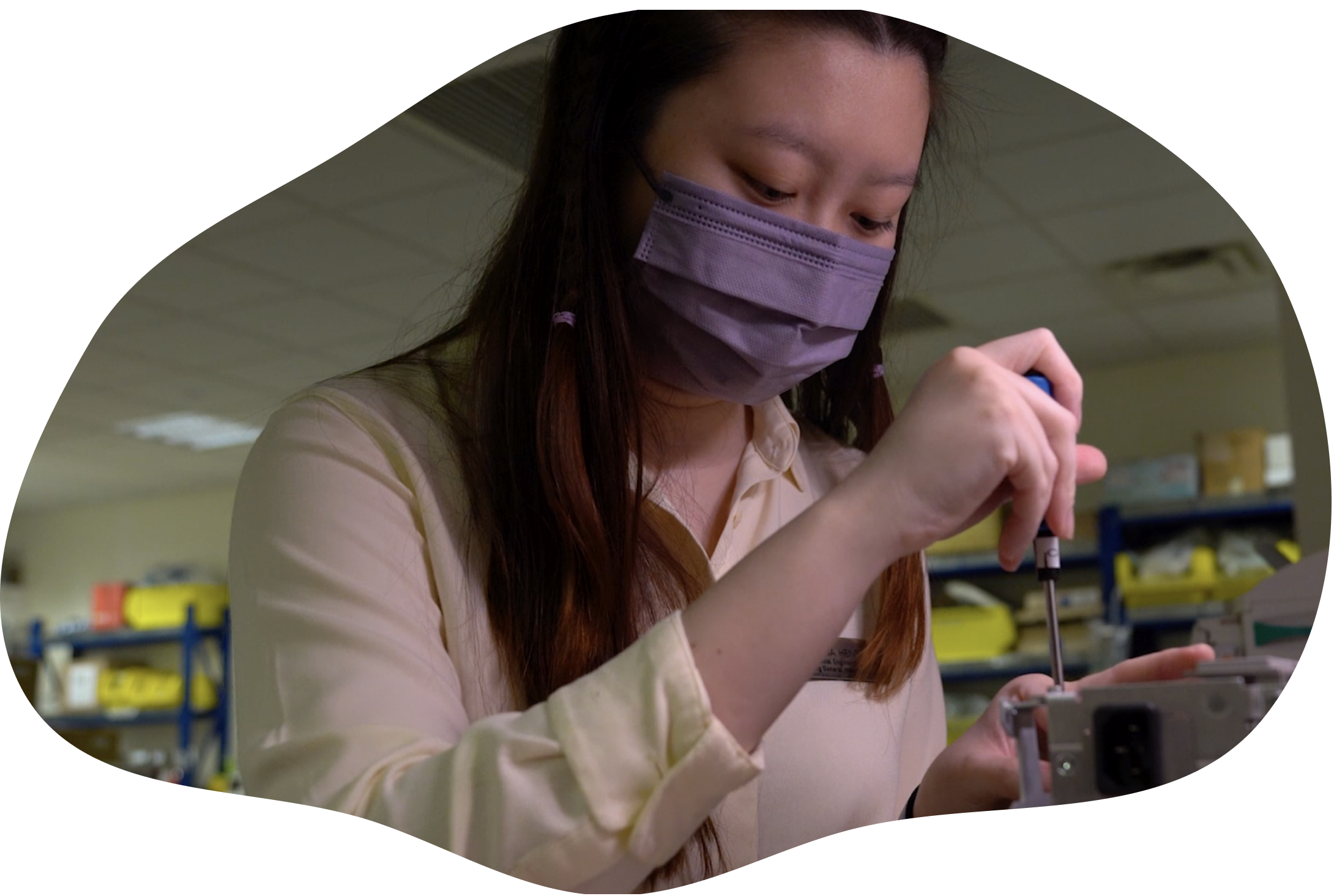
“Go in with an open mind and don't be afraid to try new stuff.”
Marcellina, Biomedical Engineer Assistant
Related Job Roles
Explore Other Programmes
Browse AllYou have bookmarked your first item!
Find it in My Discoveries with insights on your interests!